Show EOL distros:
| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: beginner level tutorials. |
| |
ゴールコールバックメソッドを使ったシンプルなアクションサーバを書く
Description: このチュートリアルは、simple_action_serverライブラリを使ってデータを平均化するアクションサーバについて扱います。この例はROSノードから入ってくるデータを処理またはデータに反応するためのアクションの使い方を示します。アクションサーバはROSノードからのデータを平均化し、ゴールはサンプル数で平均し、平均するサンプルの数であり、フィードバックはサンプル数、サンプルデータ、現在の平均、および現在の標準偏差で、結果はサンプルの要求された数の平均と標準偏差です。Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Next Tutorial: スレッドのシンプルなアクションクライアントを書く
Contents
Creating the Action Messages
Before writing an action it is important to define the goal, result, and feedback messages. The action messages are generated automatically from the .action file, for more information on action files see the actionlib documentation. This file defines the type and format of the goal, result, and feedback topics for the action. Create learning_actionlib/action/Averaging.action in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
#goal definition int32 samples --- #result definition float32 mean float32 std_dev --- #feedback int32 sample float32 data float32 mean float32 std_dev
To manually generate the message files from this file:
$ roscd learning_actionlib $ rosrun actionlib genaction.py . Averaging.action
You will see:
Generating for action Averaging
To automatically generate the message files during the make process, add the following to CMakeLists.txt (before the rosbuild_init call)
rosbuild_find_ros_package(actionlib_msgs)
include(${actionlib_msgs_PACKAGE_PATH}/cmake/actionbuild.cmake)
genaction()
Writing a Simple Server
First, create learning_actionlib/src/averaging_server.cpp in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
The Code
1 #include <ros/ros.h>
2 #include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
3 #include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h>
4 #include <learning_actionlib/AveragingAction.h>
5
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
17
18 //subscribe to the data topic of interest
19 sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", 1, &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
20 as_.start();
21 }
22
23 ~AveragingAction(void)
24 {
25 }
26
27 void goalCB()
28 {
29 // reset helper variables
30 data_count_ = 0;
31 sum_ = 0;
32 sum_sq_ = 0;
33 // accept the new goal
34 goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
35 }
36
37 void preemptCB()
38 {
39 ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
40 // set the action state to preempted
41 as_.setPreempted();
42 }
43
44 void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
45 {
46 // make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
47 if (!as_.isActive())
48 return;
49
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
59
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
79
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
91
92 int main(int argc, char** argv)
93 {
94 ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging");
95
96 AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
97 ros::spin();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
The Code Explained
Now, let's break down the code piece by piece.
actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h is the action library used from implementing simple actions.
This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file show above. This is a header generated automatically from the AveragingAction.msg file. For more information on message definitions, see the msg page.
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
In the action constructor, an action server is created. The action server takes arguments of a node handle, name of the action, and optionally an executeCB. In this example the action server is created without the arguments for the executeCB. Instead the goal and preempt callbacks are registered with the action server in the constructor for the action after the action server has been constructed.
Here a callback is setup for the data that will be processed by the action and the action server is started.
Here is the goalCB function referenced in the constructor. The callback function returns nothing and takes no arguments. When the goalCB is called the action needs to accept the goal and store any important information. If you need to see the goal before you accept it, see the SimpleActionServer(ExecuteCallbackMethod) tutorial.
This action is event driven, the action code only runs when the callbacks occur therefore a preempt callback is created to ensure that the action responds promptly to a cancel request. The callback function takes no arguments and sets preempted on the action server.
Here the analysis callback takes the message format of the subscribed data channel and checks that the action is still in an active state before continuing to process the data.
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
Here the relevant data is put into the feedback variable and then published on the feedback channel provided by the action server.
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
Once adequate data has been collected, the action server is set to success or failure. This will deactivate the action server and the analysisCB function will return immediately as discussed previously.
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
These are the protected variables of the action class. The node handle is constructed and passed into the action server during construction of the action. The action server is constructed in the constructor of the action and has been discussed above. The feedback and result messages are created for publishing in the action. The subscriber is also constructed to save the node handle.
Finally the main function, creates the action and spins the node. The action will be running and waiting to receive goals.
Compiling and Running the Action
Add the following line to your CMakeLists.txt file:
rosbuild_add_executable(averaging_server src/averaging_server.cpp)
After you have made the executable, start a roscore in a new terminal
$ roscore
And then run the action server:
$ rosrun learning_actionlib averaging_server
You will see something similar to:
[ INFO] 1250790662.410962000: Started node [/averaging], pid [29267], bound on [aqy], xmlrpc port [39746], tcpros port [49573], logging to [~/ros/ros/log/averaging_29267.log], using [real] time
To check that your action is running properly list topics being published:
$ rostopic list -v
You will see something similar to:
Published topics: * /averaging/status [actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray] 1 publisher * /averaging/result [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionResult] 1 publisher * /averaging/feedback [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionFeedback] 1 publisher * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 publisher * /rosout_agg [roslib/Log] 1 publisher Subscribed topics: * /time [unknown type] 2 subscribers * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 subscriber * /averaging/goal [unknown type] 1 subscriber * /averaging/cancel [unknown type] 1 subscriber
Alternatively you can look at the nodes:
$ rxgraph
This shows that your action server is publishing the feedback, status, and result channels as expected and subscribed to the goal and cancel channels as expected. The action server is up and running properly.
Sending a Goal to the Action Server
For the next step in using your action, you need to Ctrl-C the action server and write a threaded simple action client.
Contents
Creating the Action Messages
Before writing an action it is important to define the goal, result, and feedback messages. The action messages are generated automatically from the .action file, for more information on action files see the actionlib documentation. This file defines the type and format of the goal, result, and feedback topics for the action. Create learning_actionlib/action/Averaging.action in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
#goal definition int32 samples --- #result definition float32 mean float32 std_dev --- #feedback int32 sample float32 data float32 mean float32 std_dev
To manually generate the message files from this file:
$ roscd learning_actionlib $ rosrun actionlib genaction.py . Averaging.action
You will see:
Generating for action Averaging
To automatically generate the message files during the make process, add the following to CMakeLists.txt (before the rosbuild_init call)
rosbuild_find_ros_package(actionlib_msgs)
include(${actionlib_msgs_PACKAGE_PATH}/cmake/actionbuild.cmake)
genaction()
Writing a Simple Server
First, create learning_actionlib/src/averaging_server.cpp in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
The Code
1 #include <ros/ros.h>
2 #include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
3 #include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h>
4 #include <learning_actionlib/AveragingAction.h>
5
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
17
18 //subscribe to the data topic of interest
19 sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", 1, &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
20 as_.start();
21 }
22
23 ~AveragingAction(void)
24 {
25 }
26
27 void goalCB()
28 {
29 // reset helper variables
30 data_count_ = 0;
31 sum_ = 0;
32 sum_sq_ = 0;
33 // accept the new goal
34 goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
35 }
36
37 void preemptCB()
38 {
39 ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
40 // set the action state to preempted
41 as_.setPreempted();
42 }
43
44 void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
45 {
46 // make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
47 if (!as_.isActive())
48 return;
49
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
59
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
79
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
91
92 int main(int argc, char** argv)
93 {
94 ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging");
95
96 AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
97 ros::spin();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
The Code Explained
Now, let's break down the code piece by piece.
actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h is the action library used from implementing simple actions.
This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file show above. This is a header generated automatically from the AveragingAction.msg file. For more information on message definitions, see the msg page.
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
In the action constructor, an action server is created. The action server takes arguments of a node handle, name of the action, and optionally an executeCB. In this example the action server is created without the arguments for the executeCB. Instead the goal and preempt callbacks are registered with the action server in the constructor for the action after the action server has been constructed.
Here a callback is setup for the data that will be processed by the action and the action server is started.
Here is the goalCB function referenced in the constructor. The callback function returns nothing and takes no arguments. When the goalCB is called the action needs to accept the goal and store any important information. If you need to see the goal before you accept it, see the SimpleActionServer(ExecuteCallbackMethod) tutorial.
This action is event driven, the action code only runs when the callbacks occur therefore a preempt callback is created to ensure that the action responds promptly to a cancel request. The callback function takes no arguments and sets preempted on the action server.
Here the analysis callback takes the message format of the subscribed data channel and checks that the action is still in an active state before continuing to process the data.
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
Here the relevant data is put into the feedback variable and then published on the feedback channel provided by the action server.
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
Once adequate data has been collected, the action server is set to success or failure. This will deactivate the action server and the analysisCB function will return immediately as discussed previously.
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
These are the protected variables of the action class. The node handle is constructed and passed into the action server during construction of the action. The action server is constructed in the constructor of the action and has been discussed above. The feedback and result messages are created for publishing in the action. The subscriber is also constructed to save the node handle.
Finally the main function, creates the action and spins the node. The action will be running and waiting to receive goals.
Compiling and Running the Action
Add the following line to your CMakeLists.txt file:
rosbuild_add_executable(averaging_server src/averaging_server.cpp)
After you have made the executable, start a roscore in a new terminal
$ roscore
And then run the action server:
$ rosrun learning_actionlib averaging_server
You will see something similar to:
[ INFO] 1250790662.410962000: Started node [/averaging], pid [29267], bound on [aqy], xmlrpc port [39746], tcpros port [49573], logging to [~/ros/ros/log/averaging_29267.log], using [real] time
To check that your action is running properly list topics being published:
$ rostopic list -v
You will see something similar to:
Published topics: * /averaging/status [actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray] 1 publisher * /averaging/result [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionResult] 1 publisher * /averaging/feedback [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionFeedback] 1 publisher * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 publisher * /rosout_agg [roslib/Log] 1 publisher Subscribed topics: * /time [unknown type] 2 subscribers * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 subscriber * /averaging/goal [unknown type] 1 subscriber * /averaging/cancel [unknown type] 1 subscriber
Alternatively you can look at the nodes:
$ rxgraph
This shows that your action server is publishing the feedback, status, and result channels as expected and subscribed to the goal and cancel channels as expected. The action server is up and running properly.
Sending a Goal to the Action Server
For the next step in using your action, you need to Ctrl-C the action server and write a threaded simple action client.
Contents
Creating the Action Messages
Before writing an action it is important to define the goal, result, and feedback messages. The action messages are generated automatically from the .action file, for more information on action files see the actionlib documentation. This file defines the type and format of the goal, result, and feedback topics for the action. Create learning_actionlib/action/Averaging.action in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
#goal definition int32 samples --- #result definition float32 mean float32 std_dev --- #feedback int32 sample float32 data float32 mean float32 std_dev
To manually generate the message files from this file:
$ roscd learning_actionlib $ rosrun actionlib_msgs genaction.py . Averaging.action
You will see:
Generating for action Averaging
To automatically generate the message files during the make process, add the following to CMakeLists.txt (before the rosbuild_init call)
rosbuild_find_ros_package(actionlib_msgs)
include(${actionlib_msgs_PACKAGE_PATH}/cmake/actionbuild.cmake)
genaction()
Writing a Simple Server
First, create learning_actionlib/src/averaging_server.cpp in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
The Code
1 #include <ros/ros.h>
2 #include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
3 #include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h>
4 #include <learning_actionlib/AveragingAction.h>
5
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
17
18 //subscribe to the data topic of interest
19 sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", 1, &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
20 as_.start();
21 }
22
23 ~AveragingAction(void)
24 {
25 }
26
27 void goalCB()
28 {
29 // reset helper variables
30 data_count_ = 0;
31 sum_ = 0;
32 sum_sq_ = 0;
33 // accept the new goal
34 goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
35 }
36
37 void preemptCB()
38 {
39 ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
40 // set the action state to preempted
41 as_.setPreempted();
42 }
43
44 void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
45 {
46 // make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
47 if (!as_.isActive())
48 return;
49
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
59
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
79
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
91
92 int main(int argc, char** argv)
93 {
94 ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging");
95
96 AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
97 ros::spin();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
The Code Explained
Now, let's break down the code piece by piece.
actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h is the action library used from implementing simple actions.
This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file show above. This is a header generated automatically from the AveragingAction.msg file. For more information on message definitions, see the msg page.
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
In the action constructor, an action server is created. The action server takes arguments of a node handle, name of the action, and optionally an executeCB. In this example the action server is created without the arguments for the executeCB. Instead the goal and preempt callbacks are registered with the action server in the constructor for the action after the action server has been constructed.
Here a callback is setup for the data that will be processed by the action and the action server is started.
Here is the goalCB function referenced in the constructor. The callback function returns nothing and takes no arguments. When the goalCB is called the action needs to accept the goal and store any important information. If you need to see the goal before you accept it, see the SimpleActionServer(ExecuteCallbackMethod) tutorial.
This action is event driven, the action code only runs when the callbacks occur therefore a preempt callback is created to ensure that the action responds promptly to a cancel request. The callback function takes no arguments and sets preempted on the action server.
Here the analysis callback takes the message format of the subscribed data channel and checks that the action is still in an active state before continuing to process the data.
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
Here the relevant data is put into the feedback variable and then published on the feedback channel provided by the action server.
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
Once adequate data has been collected, the action server is set to success or failure. This will deactivate the action server and the analysisCB function will return immediately as discussed previously.
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
These are the protected variables of the action class. The node handle is constructed and passed into the action server during construction of the action. The action server is constructed in the constructor of the action and has been discussed above. The feedback and result messages are created for publishing in the action. The subscriber is also constructed to save the node handle.
Finally the main function, creates the action and spins the node. The action will be running and waiting to receive goals.
Compiling and Running the Action
Add the following line to your CMakeLists.txt file:
rosbuild_add_executable(averaging_server src/averaging_server.cpp)
After you have made the executable, start a roscore in a new terminal
$ roscore
And then run the action server:
$ rosrun learning_actionlib averaging_server
You will see something similar to:
[ INFO] 1250790662.410962000: Started node [/averaging], pid [29267], bound on [aqy], xmlrpc port [39746], tcpros port [49573], logging to [~/ros/ros/log/averaging_29267.log], using [real] time
To check that your action is running properly list topics being published:
$ rostopic list -v
You will see something similar to:
Published topics: * /averaging/status [actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray] 1 publisher * /averaging/result [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionResult] 1 publisher * /averaging/feedback [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionFeedback] 1 publisher * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 publisher * /rosout_agg [roslib/Log] 1 publisher Subscribed topics: * /time [unknown type] 2 subscribers * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 subscriber * /averaging/goal [unknown type] 1 subscriber * /averaging/cancel [unknown type] 1 subscriber
Alternatively you can look at the nodes:
$ rxgraph
This shows that your action server is publishing the feedback, status, and result channels as expected and subscribed to the goal and cancel channels as expected. The action server is up and running properly.
Sending a Goal to the Action Server
For the next step in using your action, you need to Ctrl-C the action server and write a threaded simple action client.
Contents
Creating the Action Messages
Before writing an action it is important to define the goal, result, and feedback messages. The action messages are generated automatically from the .action file, for more information on action files see the actionlib documentation. This file defines the type and format of the goal, result, and feedback topics for the action. Create learning_actionlib/action/Averaging.action in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
#goal definition int32 samples --- #result definition float32 mean float32 std_dev --- #feedback int32 sample float32 data float32 mean float32 std_dev
To manually generate the message files from this file:
$ roscd learning_actionlib $ rosrun actionlib_msgs genaction.py -o msg/ action/Averaging.action
You will see:
Generating for action Averaging
To automatically generate the message files during the make process, add the following to CMakeLists.txt (before the rosbuild_init call)
rosbuild_find_ros_package(actionlib_msgs)
include(${actionlib_msgs_PACKAGE_PATH}/cmake/actionbuild.cmake)
genaction()
Writing a Simple Server
First, create learning_actionlib/src/averaging_server.cpp in your favorite editor, and place the following inside it:
The Code
1 #include <ros/ros.h>
2 #include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
3 #include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h>
4 #include <learning_actionlib/AveragingAction.h>
5
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
17
18 //subscribe to the data topic of interest
19 sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", 1, &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
20 as_.start();
21 }
22
23 ~AveragingAction(void)
24 {
25 }
26
27 void goalCB()
28 {
29 // reset helper variables
30 data_count_ = 0;
31 sum_ = 0;
32 sum_sq_ = 0;
33 // accept the new goal
34 goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
35 }
36
37 void preemptCB()
38 {
39 ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
40 // set the action state to preempted
41 as_.setPreempted();
42 }
43
44 void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
45 {
46 // make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
47 if (!as_.isActive())
48 return;
49
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
59
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
79
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
91
92 int main(int argc, char** argv)
93 {
94 ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging");
95
96 AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
97 ros::spin();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
The Code Explained
Now, let's break down the code piece by piece.
actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h is the action library used from implementing simple actions.
This includes action message generated from the Averaging.action file show above. This is a header generated automatically from the AveragingAction.msg file. For more information on message definitions, see the msg page.
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
In the action constructor, an action server is created. The action server takes arguments of a node handle, name of the action, and optionally an executeCB. In this example the action server is created without the arguments for the executeCB. Instead the goal and preempt callbacks are registered with the action server in the constructor for the action after the action server has been constructed.
Here a callback is setup for the data that will be processed by the action and the action server is started.
Here is the goalCB function referenced in the constructor. The callback function returns nothing and takes no arguments. When the goalCB is called the action needs to accept the goal and store any important information. If you need to see the goal before you accept it, see the SimpleActionServer(ExecuteCallbackMethod) tutorial.
This action is event driven, the action code only runs when the callbacks occur therefore a preempt callback is created to ensure that the action responds promptly to a cancel request. The callback function takes no arguments and sets preempted on the action server.
Here the analysis callback takes the message format of the subscribed data channel and checks that the action is still in an active state before continuing to process the data.
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
Here the relevant data is put into the feedback variable and then published on the feedback channel provided by the action server.
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
Once adequate data has been collected, the action server is set to success or failure. This will deactivate the action server and the analysisCB function will return immediately as discussed previously.
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
These are the protected variables of the action class. The node handle is constructed and passed into the action server during construction of the action. The action server is constructed in the constructor of the action and has been discussed above. The feedback and result messages are created for publishing in the action. The subscriber is also constructed to save the node handle.
Finally the main function, creates the action and spins the node. The action will be running and waiting to receive goals.
Compiling and Running the Action
Add the following line to your CMakeLists.txt file:
rosbuild_add_executable(averaging_server src/averaging_server.cpp)
After you have made the executable, start a roscore in a new terminal
$ roscore
And then run the action server:
$ rosrun learning_actionlib averaging_server
You will see something similar to:
[ INFO] 1250790662.410962000: Started node [/averaging], pid [29267], bound on [aqy], xmlrpc port [39746], tcpros port [49573], logging to [~/ros/ros/log/averaging_29267.log], using [real] time
To check that your action is running properly list topics being published:
$ rostopic list -v
You will see something similar to:
Published topics: * /averaging/status [actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray] 1 publisher * /averaging/result [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionResult] 1 publisher * /averaging/feedback [actionlib_tutorials/AveragingActionFeedback] 1 publisher * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 publisher * /rosout_agg [roslib/Log] 1 publisher Subscribed topics: * /time [unknown type] 2 subscribers * /rosout [roslib/Log] 1 subscriber * /averaging/goal [unknown type] 1 subscriber * /averaging/cancel [unknown type] 1 subscriber
Alternatively you can look at the nodes:
$ rxgraph
This shows that your action server is publishing the feedback, status, and result channels as expected and subscribed to the goal and cancel channels as expected. The action server is up and running properly.
Sending a Goal to the Action Server
For the next step in using your action, you need to Ctrl-C the action server and write a threaded simple action client.
アクションメッセージを生成する
actionを書く前に、ゴール、結果、およびフィードバックのメッセージを定義することは重要です。actionメッセージは.actionファイルから自動的に生成されます。actionファイルの詳細については、actionlibドキュメンテーションにあります。このファイルはactionについてのゴール、結果、およびフィードバックのトピックのタイプとフォーマットを定義します。エディタでlearning_actionlib/action/Averaging.actionを作成し、以下を書き込みます:
#goal definition int32 samples --- #result definition float32 mean float32 std_dev --- #feedback int32 sample float32 data float32 mean float32 std_dev
このファイルから手動でメッセージファイルを生成するには:
$ roscd learning_actionlib $ rosrun actionlib_msgs genaction.py -o msg/ action/Averaging.action
以下の出力が見えるでしょう:
Generating for action Averaging
makeプロセスで自動的にメッセージファイルを生成するために、以下をCMakeLists.txtに追加します:
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS actionlib std_msgs message_generation) add_action_files(DIRECTORY action FILES Averaging.action) generate_messages(DEPENDENCIES std_msgs actionlib_msgs)
そして、catkin_makeを実行します:
$ cd %TOP_DIR_YOUR_CATKIN_WORKSPACE% $ catkin_make
シンプルなサーバを書く
まず、エディタでlearning_actionlib/src/averaging_server.cppを作成し、以下を書き込みます:
コード
1 #include <ros/ros.h>
2 #include <std_msgs/Float32.h>
3 #include <actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h>
4 #include <learning_actionlib/AveragingAction.h>
5
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
17
18 //subscribe to the data topic of interest
19 sub_ = nh_.subscribe("/random_number", 1, &AveragingAction::analysisCB, this);
20 as_.start();
21 }
22
23 ~AveragingAction(void)
24 {
25 }
26
27 void goalCB()
28 {
29 // reset helper variables
30 data_count_ = 0;
31 sum_ = 0;
32 sum_sq_ = 0;
33 // accept the new goal
34 goal_ = as_.acceptNewGoal()->samples;
35 }
36
37 void preemptCB()
38 {
39 ROS_INFO("%s: Preempted", action_name_.c_str());
40 // set the action state to preempted
41 as_.setPreempted();
42 }
43
44 void analysisCB(const std_msgs::Float32::ConstPtr& msg)
45 {
46 // make sure that the action hasn't been canceled
47 if (!as_.isActive())
48 return;
49
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
59
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
79
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
91
92 int main(int argc, char** argv)
93 {
94 ros::init(argc, argv, "averaging");
95
96 AveragingAction averaging(ros::this_node::getName());
97 ros::spin();
98
99 return 0;
100 }
コード解説
では、一つずつコードを分析していきましょう。
actionlib/server/simple_action_server.hはシンプルなactionを実装する際に使えるactionライブラリです。
これは上で示したAveraging.actionファイルで生成されたactionメッセージをインクルードします。これはAveragingAction.msg ファイルから自動的に生成されたヘッダファイルです。メッセージ定義の詳細は msg ページにあります。
6 class AveragingAction
7 {
8 public:
9
10 AveragingAction(std::string name) :
11 as_(nh_, name, false),
12 action_name_(name)
13 {
14 //register the goal and feeback callbacks
15 as_.registerGoalCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::goalCB, this));
16 as_.registerPreemptCallback(boost::bind(&AveragingAction::preemptCB, this));
actionのコンストラクタの中で、actionサーバは生成されます。actionサーバは、ノードハンドル、actionの名前、オプションでexecuteCB(コールバック)を引数として取ります。この例では、actionサーバはexecuteCBの引数無しで生成されます。そのかわりにゴールとpreemptコールバックは、actionサーバが構築された後にactionのコンストラクタの中でactionサーバに登録されます。
ここではactionによって処理されるデータ用にコールバックを設定し、そしてactionサーバを開始しています。
これはgoalCB関数でコンストラクタ内で参照されます。このコールバック関数は戻り値が無く、引数も取りません。goalCBが呼ばれる時actionはゴールを受け付け、重要な情報を全て格納します。もし先にゴールを見る必要がある場合は、SimpleActionServer(ExecuteCallbackMethod) チュートリアルを参考にしてください。
このactionはイベンドドリブンで、actionのコードはコールバックが起きた時だけ走るので、preemptコールバックは、actionが取り消し要求へ即座に応答することを保証するために生成されます。コールバック関数は引数を取らず、actionサーバの状態をpreemptedに設定します。
analysisコールバックは購読するデータチャネルのメッセージフォーマットを取り、データを処理し続ける前にactionがまだアクティブな状態にあるかをチェックします。
50 data_count_++;
51 feedback_.sample = data_count_;
52 feedback_.data = msg->data;
53 //compute the std_dev and mean of the data
54 sum_ += msg->data;
55 feedback_.mean = sum_ / data_count_;
56 sum_sq_ += pow(msg->data, 2);
57 feedback_.std_dev = sqrt(fabs((sum_sq_/data_count_) - pow(feedback_.mean, 2)));
58 as_.publishFeedback(feedback_);
ここで、関連データはフィードバック変数に入れられ、それからactionサーバによって提供されたフィードバックチャンネルの上に配信されます。
60 if(data_count_ > goal_)
61 {
62 result_.mean = feedback_.mean;
63 result_.std_dev = feedback_.std_dev;
64
65 if(result_.mean < 5.0)
66 {
67 ROS_INFO("%s: Aborted", action_name_.c_str());
68 //set the action state to aborted
69 as_.setAborted(result_);
70 }
71 else
72 {
73 ROS_INFO("%s: Succeeded", action_name_.c_str());
74 // set the action state to succeeded
75 as_.setSucceeded(result_);
76 }
77 }
78 }
適正なデータが収集されると、actionサーバが成功か失敗かをセットします。これでactionサーバは非活性化しますし、以前に議論したように、analysisCB関数はすぐに戻りを返すことになります。
80 protected:
81
82 ros::NodeHandle nh_;
83 actionlib::SimpleActionServer<learning_actionlib::AveragingAction> as_;
84 std::string action_name_;
85 int data_count_, goal_;
86 float sum_, sum_sq_;
87 learning_actionlib::AveragingFeedback feedback_;
88 learning_actionlib::AveragingResult result_;
89 ros::Subscriber sub_;
90 };
これらはactionクラスのprotectedな変数です。ノードハンドルは構築され、actionの構築中にactionサーバに渡されます。前述の通りactionのコンストラクタの中でactionサーバは構築されます。配信するためのフィードバックと結果のメッセージ変数がここで作られます。購読の変数もノードハンドルを保存する形で構築されます。
最後は、メイン関数です。メイン関数はactionを生成し、シングルスレッドのループを回します。actionは実行しながら、ゴールを受け取るのを待ちます。
アクションをコンパイルし実行する
CMakeLists.txtファイルに、以下の2行を加えます:
add_executable(averaging_server src/averaging_server.cpp)
target_link_libraries(averaging_server ${catkin_LIBRARIES})catkin_makeで実行ファイルを生成したら、新しいターミナルでroscoreをスタートさせます。
$ roscore
そしてactionサーバを起動します:
$ rosrun learning_actionlib averaging_server
以下のような出力が見えるでしょう:
[ INFO] 1250790662.410962000: Started node [/averaging], pid [29267], bound on [aqy], xmlrpc port [39746], tcpros port [49573], logging to [~/ros/ros/log/averaging_29267.log], using [real] time
actionが正しく動いていることをチェックするために、配信されてるトピックをリストします:
$ rostopic list -v
以下の様な出力が見えるでしょう:
Published topics: * /averaging/feedback [learning_actionlib/AveragingActionFeedback] 1 publisher * /averaging/status [actionlib_msgs/GoalStatusArray] 1 publisher * /rosout [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 1 publisher * /averaging/result [learning_actionlib/AveragingActionResult] 1 publisher * /rosout_agg [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 1 publisher Subscribed topics: * /random_number [std_msgs/Float32] 1 subscriber * /averaging/goal [learning_actionlib/AveragingActionGoal] 1 subscriber * /averaging/cancel [actionlib_msgs/GoalID] 1 subscriber * /rosout [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 1 subscriber
上記の代わりに、ノードを見ることができます:
$ rosrun rqt_graph rqt_graph &
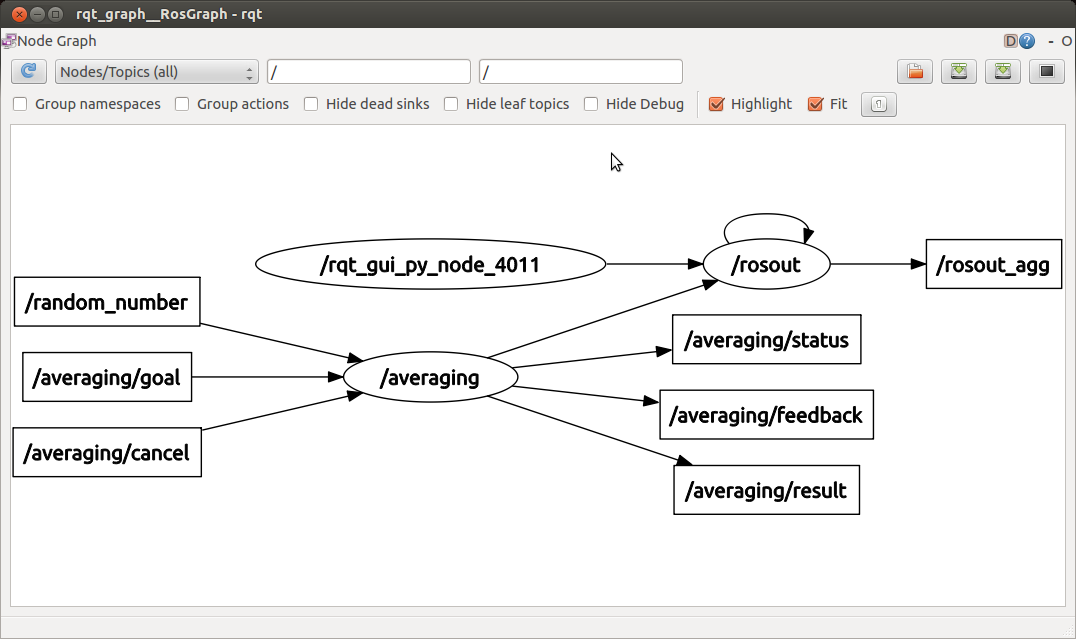
これは、actionサーバーが、期待通りにフィードバック、ステータス、結果のチャネルを配信し、ゴールとcancelチャネルを購読していることを示しています。actionサーバは起動し、正しく動作しています。
ゴールをアクションサーバに送る
actionを使った次のステップのために、Ctrl-Cでactionサーバを停止しておく必要があります。次はwrite a threaded simple action clientです。







