| |
Wandering robot FSM example
Description: Writing FSM's for a wandering robotKeywords: FSM, decision_making_examples
Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Contents
Running the example
roslaunch decision_making_examples fsm_wandering.launch
Overview
In this tutorial we will cover creation of a simple wandering algorithm using a finite-state machine as depicted below. The source code described here can be found in decision_making_examples packages (src/Wandering.cpp).
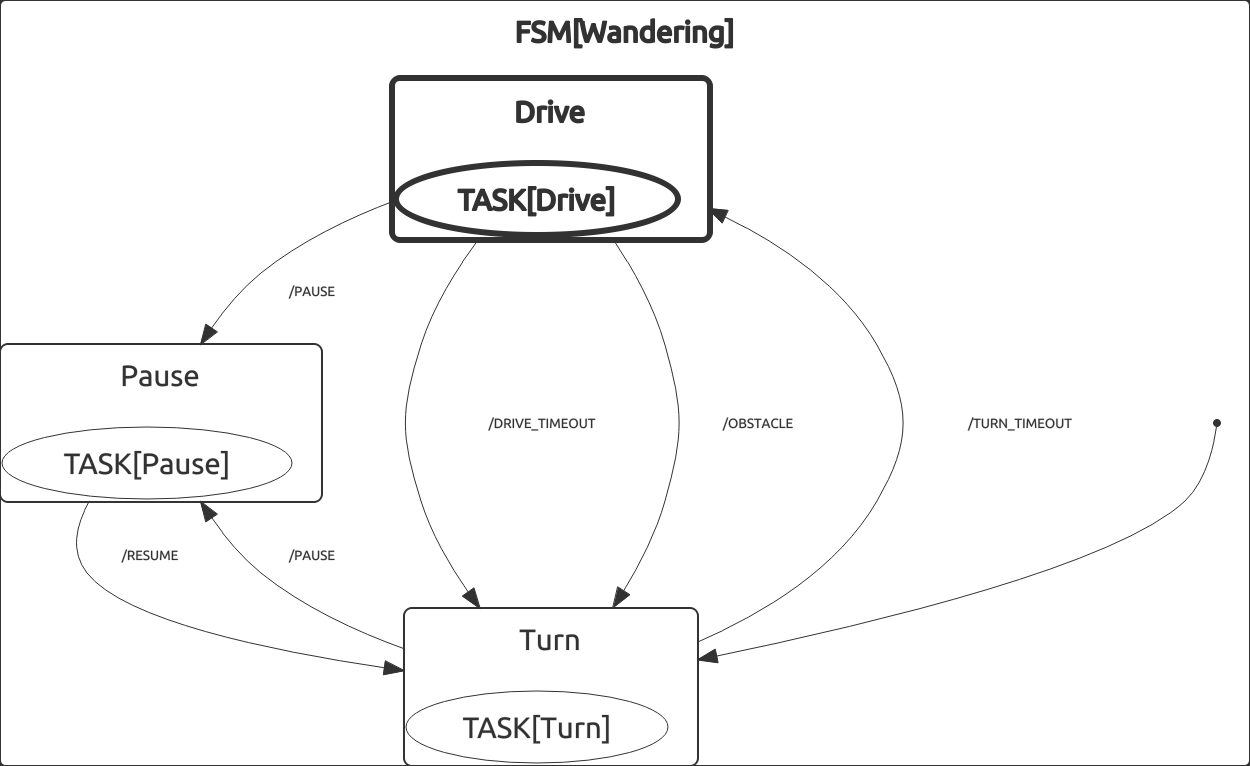
The FSM
1 FSM(Wandering)
2 {
3 FSM_STATES
4 {
5 Drive,
6 Turn,
7 Pause
8 }
9 FSM_START(Turn)
10 FSM_BGN
11 {
12 FSM_STATE(Turn)
13 {
14 FSM_CALL_TASK(Turn)
15
16 FSM_TRANSITIONS
17 {
18 FSM_ON_EVENT(/TURN_TIMEOUT, FSM_NEXT(Drive))
19 FSM_ON_EVENT(/PAUSE, FSM_NEXT(Pause))
20 }
21 }
22 FSM_STATE(Drive)
23 {
24 FSM_CALL_TASK(Drive)
25
26 FSM_TRANSITIONS
27 {
28 FSM_ON_EVENT(/DRIVE_TIMEOUT, FSM_NEXT(Turn))
29 FSM_ON_EVENT(/OBSTACLE, FSM_NEXT(Turn))
30 FSM_ON_EVENT(/PAUSE, FSM_NEXT(Pause))
31 }
32 }
33 FSM_STATE(Pause)
34 {
35 FSM_CALL_TASK(Pause)
36
37 FSM_TRANSITIONS
38 {
39 FSM_ON_EVENT(/RESUME, FSM_NEXT(Turn))
40 }
41 }
42 }
43 FSM_END
44 }
Generated SCXML
1 <?xml version="1.0"?>
2 <scxml>
3 <state name="Wandering" initialstate="Turn" id="/Wandering">
4 <state name="Turn" id="/Wandering/Turn">
5 <state name="TASK[Turn]" id="/Wandering/Turn/Turn" />
6 <transition event="/TURN_TIMEOUT" target="/Wandering/Drive"></transition>
7 <transition event="/PAUSE" target="/Wandering/Pause"></transition>
8 </state>
9 <state name="Drive" id="/Wandering/Drive">
10 <state name="TASK[Drive]" id="/Wandering/Drive/Drive" />
11 <transition event="/DRIVE_TIMEOUT" target="/Wandering/Turn"></transition>
12 <transition event="/OBSTACLE" target="/Wandering/Turn"></transition>
13 <transition event="/PAUSE" target="/Wandering/Pause"></transition>
14 </state>
15 <state name="Pause" id="/Wandering/Pause">
16 <state name="TASK[Pause]" id="/Wandering/Pause/Pause" />
17 <transition event="/RESUME" target="/Wandering/Turn"></transition>
18 </state>
19 </state>
20 </scxml>
Tasks
As you can see, we use three states: Drive, Turn and Pause. For each state we implement corresponding task: driveTask(), turnTask() and pauseTask().
Drive task
Drive task tells the robot to drive straight for a random amount of time. Note that we use preemptive wait, because we can receive an /OBSTACLE event which tells the robot must stop.
1 decision_making::TaskResult driveTask(string name, const FSMCallContext& context, EventQueue& eventQueue) {
2 ROS_INFO("Driving...");
3
4 double timeToDriveMs = _randomizer.uniformInteger(4000, 8000);
5
6 geometry_msgs::Twist forwardMessage;
7 forwardMessage.linear.x = 2;
8 _velocityPublisher.publish(forwardMessage);
9
10 /**
11 * Preemptive wait
12 */
13 for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
14 if (eventQueue.isTerminated()) {
15 ROS_INFO("Obstacle!");
16 return TaskResult::TERMINATED();
17 }
18
19 boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::milliseconds(timeToDriveMs / 100.0));
20 }
21
22 eventQueue.riseEvent("/DRIVE_TIMEOUT");
23 return TaskResult::SUCCESS();
24 }
Turn task
This task turns the robot in random direction. Here we don't have to use preemptive wait, because turn state can be completed with a /TIMEOUT event.
1 decision_making::TaskResult turnTask(string name, const FSMCallContext& context, EventQueue& eventQueue) {
2 ROS_INFO("Turning...");
3
4 bool turnRight = _randomizer.uniformInteger(0, 1);
5 int timeToTurnMs = _randomizer.uniformInteger(2000, 4000);
6
7 geometry_msgs::Twist turnMessage;
8 turnMessage.angular.z = 2 * (turnRight ? 1 : -1);
9 _velocityPublisher.publish(turnMessage);
10
11 boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::milliseconds(timeToTurnMs));
12
13 eventQueue.riseEvent("/TURN_TIMEOUT");
14 return decision_making::TaskResult::SUCCESS();
15 }
Pause task
Here we just say the robot to stop.
Tasks registration
As you may have noticed, in the state machine we call for tasks Turn, Drive and Pause, but the actual names of task methods are turnTask, driveTask and pauseTask, so we need to bind task name to actual method:
Events
/OBSTACLE
TurnTask and DriveTask raise TIMEOUT event upon completion, but the /OBSTACLE event must come from an external source.
The external source in our case, is the onLaserScanMessage callback:
This is just an example of how you can raise the /OBSTACLE event, of cause you have to implement a better algorithm in real wandering.
/PAUSE and /RESUME
You can raise these two events by publishing a string to events topic:
rostopic pub /decision_making/wandering/events std_msgs/String "data: '/PAUSE'"
or
rostopic pub /decision_making/wandering/events std_msgs/String "data: '/RESUME'"







