| |
Setting up Dynamic Reconfigure for a Node (python)
Description: How to make a node dynamically reconfigureable in pythonTutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Next Tutorial: Using the Dynamic Reconfigure Python Client
Show EOL distros:
Contents
The Code
Since we have already created a cfg file in the last tutorial we'll dive right in to the code. Go back to our dynamic_tutorials package, create a new directory called nodes, and another directory called src. In the nodes directory create a file called server.py. Drop the following code into server.py:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 PACKAGE = 'dynamic_tutorials'
4 import roslib;roslib.load_manifest(PACKAGE)
5 import rospy
6
7 from dynamic_reconfigure.server import Server
8 from dynamic_tutorials.cfg import TutorialsConfig
9
10 def callback(config, level):
11 rospy.loginfo("""Reconfigure Request: {int_param}, {double_param},\
12 {str_param}, {bool_param}, {size}""".format(**config))
13 return config
14
15 if __name__ == "__main__":
16 rospy.init_node("dynamic_tutorials", anonymous = True)
17
18 srv = Server(TutorialsConfig, callback)
19 rospy.spin()
The Breakdown
Let's take a closer look at server.py:
These first few lines are pretty simply we just set up ROS and import dynamic_reconfigure as well as our config type.
Here we define a callback to be called when the configuration is updated, for the purposes of this tutorial we will simply print out the updated configuration.
Lastly we initialize our node, construct a server, passing it our config type and our callback function, and spin the node.
Run It!
First we need to make the node executable:
chmod +x nodes/server.py
Now rosrun the node and the launch the reconfigure_gui using:
rosrun dynamic_reconfigure reconfigure_gui
You should see a window that looks something like this pop up. 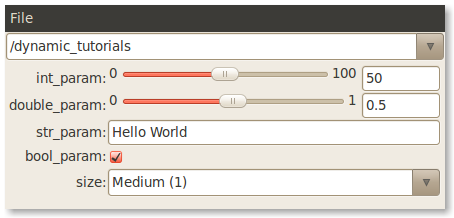
And you're done! You've just built your first dynamically reconfigure-able node.
Contents
The Code
Since we have already created a cfg file in the last tutorial we'll dive right in to the code. Go back to our dynamic_tutorials package, create a new directory called nodes, and another directory called src. In the nodes directory create a file called server.py. Drop the following code into server.py:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 import rospy
4
5 from dynamic_reconfigure.server import Server
6 from dynamic_tutorials.cfg import TutorialsConfig
7
8 def callback(config, level):
9 rospy.loginfo("""Reconfigure Request: {int_param}, {double_param},\
10 {str_param}, {bool_param}, {size}""".format(**config))
11 return config
12
13 if __name__ == "__main__":
14 rospy.init_node("dynamic_tutorials", anonymous = False)
15
16 srv = Server(TutorialsConfig, callback)
17 rospy.spin()
The Breakdown
Let's take a closer look at server.py:
These first few lines are pretty simply we just set up ROS and import dynamic_reconfigure as well as our config type. The name TutorialsConfig is automatically generated by appending Config to the 3rd argument in gen.generate (see the previous tutorial).
Here we define a callback to be called when the configuration is updated, for the purposes of this tutorial we will simply print out the updated configuration.
The callback may edit the config object before returning it. For example, if a user sets conflicting parameters the callback should set it to a valid state.
Lastly we initialize our node, construct a server, passing it our config type and our callback function, and spin the node.
Run It!
First we need to make the node executable:
chmod +x nodes/server.py
First, make sure you have the rqt reconfigure plugin installed:
sudo apt-get install ros-DISTRO-rqt-reconfigure
where DISTRO is indigo, jade, or whatever you are using.
Now, rosrun the node and the launch the reconfigure_gui using:
rosrun rqt_gui rqt_gui -s reconfigure
You should see a window that looks something like this pop up. 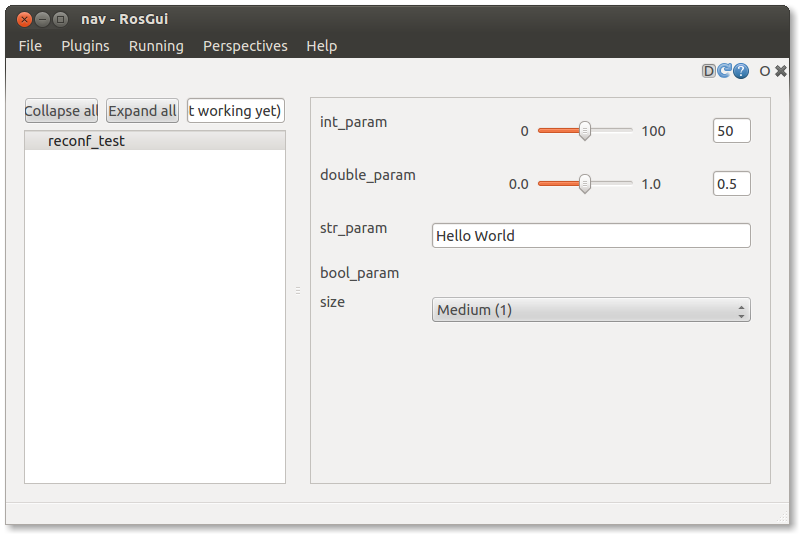
And you're done! You've just built your first dynamically reconfigure-able node.







