| |
"Checkpoint Zukunft" Care-O-bot Introduction
Description: In this tutorial, we will get to know Care-O-bot and some of its capabilities. We will start by teleoperating the robot. Afterwards, we will use the autonomous navigation functionality. If time permits, we will also explore robot perception.Tutorial Level: BEGINNER
Contents
Care-O-bot overview
Before we start with the exercises, we will first examine the robot together, in an interactive session.
Teleoperating the robot
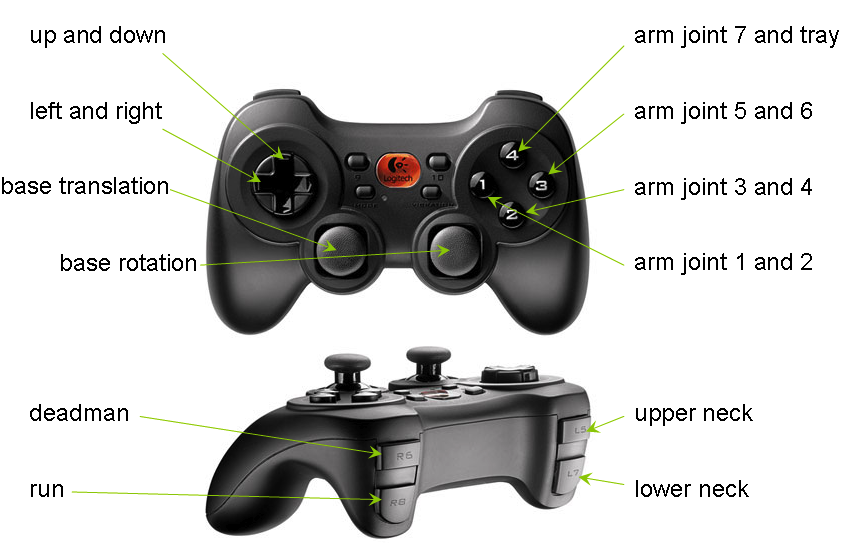
The most simple way to interact with the robot is by using the joystick to navigate the robot through a room. Use the buttons as described below to move around.
To be able to use the joystick the deadman_button has to be pressed all the time, as soon as the button is released a stop will be send to all hardware components. Have a look at the following image to see which buttons command which components.
For moving the base: Hold the deadman button and use the base rotation and translation axis to move the base.
Navigation
In this exercise, we will let the robot navigate autonomously in the environment, avoiding obstacles.
Start cob_navigation_global navigation:
ssh -X cz-group1@cob3-3-pc1 roslaunch cob_navigation_global 2dnav_ros_dwa.launch robot:=cob3-6 robot_env:=ipa-apartment
Start rviz visualisation by opening a new terminal:
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://cob3-3-pc1:11311 roslaunch cob_navigation_global rviz.launch
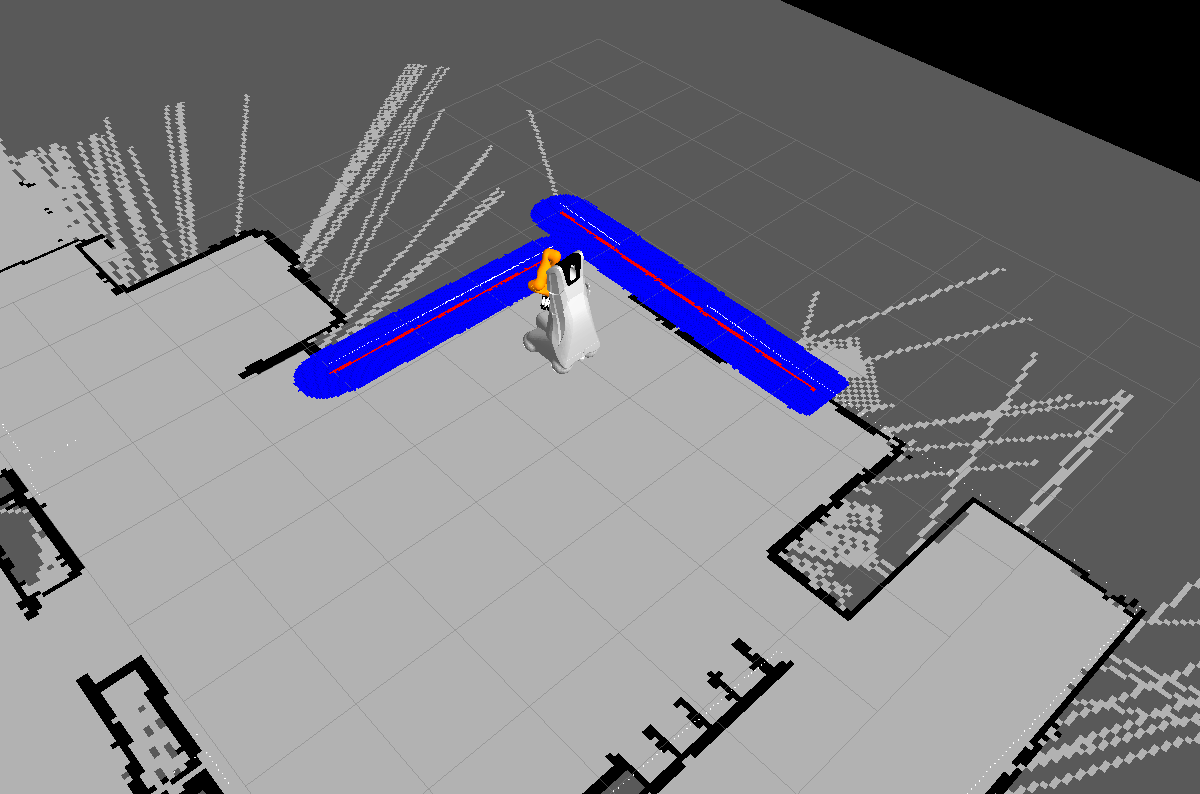
Localise the robot with giving it an estimated starting pose using the "2D Pose Estimate" button.
Use the "2D Nav Goal" button in rviz to specify a navigation goal and watch the robot moving. The robot should move towards your specified target pose avoiding obstacles which could be in the way. Detected obstacles will be highlighted in red and an inflated safety radius in blue. Try to
- move the robot into a corner using the laser scanners as a reference
- move the robot in front of the coffee machine
- move the robot directly into another room crossing doors
Run the exploration script
ssh -X cz-group1@cob3-3-pc1 rosrun cob_task_coordination_tutorials explore_groupX.py
You should see the robot driving around in the environment . As soon as the robot arrives there it will start to search for objects. If some objects could be found, the robot will announce their names and continue to drive to the next target pose.
The image below shows the simple state machine which is active in this task. 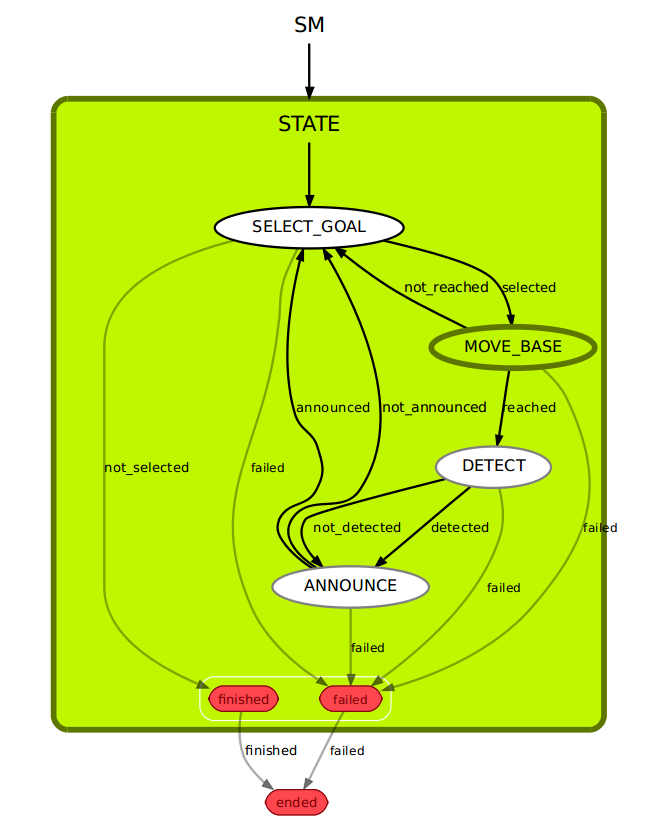
If you want to visualise the current state you can use smach_viewer.
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://cob3-3-pc1:11311 rosrun smach_viewer smach_viewer.py
You can use image_view to see what the robot camera is currently looking at.
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://cob3-3-pc1:11311 rosrun image_view image_view image:=/object_detection/image
Modify the task
Adjust the exploration behaviour
Your task is to adapt the exploration behaviour in a way that the robot doesn't move to randomly selected target poses, but for example:
- in a way that the robot goes around the table in a circle, always pointing towards the table.
- in a way that the robot goes around the table in a circle, always pointing towards the table.
- in a way that the robot moves on target positions along the walls, always pointing towards the walls.
To modify the behaviour you will need to adjust the SelectNavigationGoal state in the file cob_task_coordination_tutorials/scripts/explore_groupX.py.
1 def execute(self, userdata):
2 # defines
3 x_min = 0
4 x_max = 4.0
5 x_increment = 2
6 y_min = -4.0
7 y_max = 0.0
8 y_increment = 2
9 th_min = -3.14
10 th_max = 3.14
11 th_increment = 2*3.1414926/4
12
13 # generate new list of poses, if list is empty
14 # this will just spawn a rectangular grid
15 if len(self.goals) == 0:
16 x = x_min
17 y = y_min
18 th = th_min
19 while x <= x_max:
20 while y <= y_max:
21 while th <= th_max:
22 pose = []
23 pose.append(x) # x
24 pose.append(y) # y
25 pose.append(th) # th
26 self.goals.append(pose)
27 th += th_increment
28 y += y_increment
29 th = th_min
30 x += x_increment
31 y = y_min
32 th = th_min
33
34 # define here how to handle list of poses
35 #userdata.base_pose = self.goals.pop() # takes last element out of list
36 userdata.base_pose = [0,1,0]
37
38 return 'selected'







