Author: Jordi Pages < jordi.pages@pal-robotics.com >
Maintainer: Sara Cooper < sara.cooper@pal-robotics.com >
Support: ari-support@pal-robotics.com
Source: https://github.com/pal-robotics/ari_tutorials.git
| |
Planning in joint space
Description: How to reach a given joint space configuration using motion planning based on MoveIt!Keywords: Motion planning, joint states, forward kinematics
Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Next Tutorial: Planning in cartesian space

Contents
Purpose
This tutorial shows how to use MoveIt! in order to bring the left arm group of joints of ARI to a desired joint space configuration ensuring joint limit avoidance and self-collision avoidance. The example is given in C++.
Pre-requisites
First make sure that the tutorials are properly installed along with the ARI simulation, as shown in the Tutorials Installation Section.
Execution
First open two consoles and source the public simulation workspace as follows:
$ cd ~/ari_public_ws $ source ./devel/setup.bash
Launching the simulation
In the first console launch the following simulation
roslaunch ari_gazebo ari_gazebo.launch public_sim:=true
Gazebo will show up with ARI.
Launching the nodes
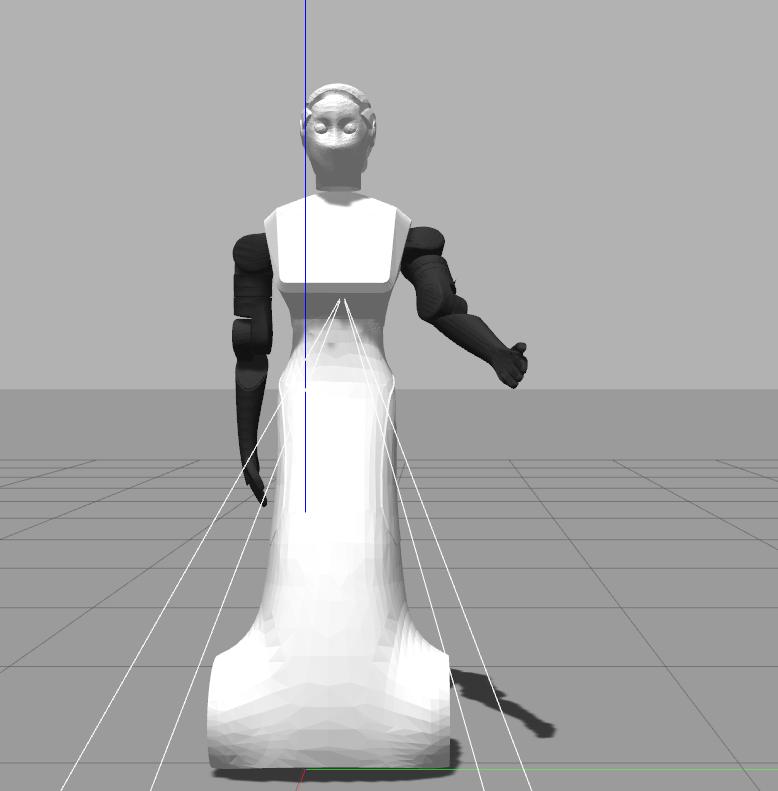
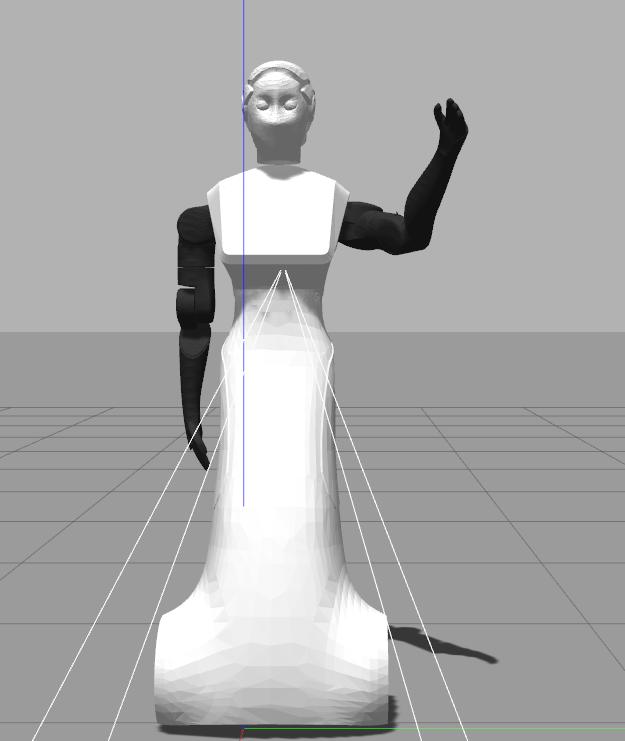
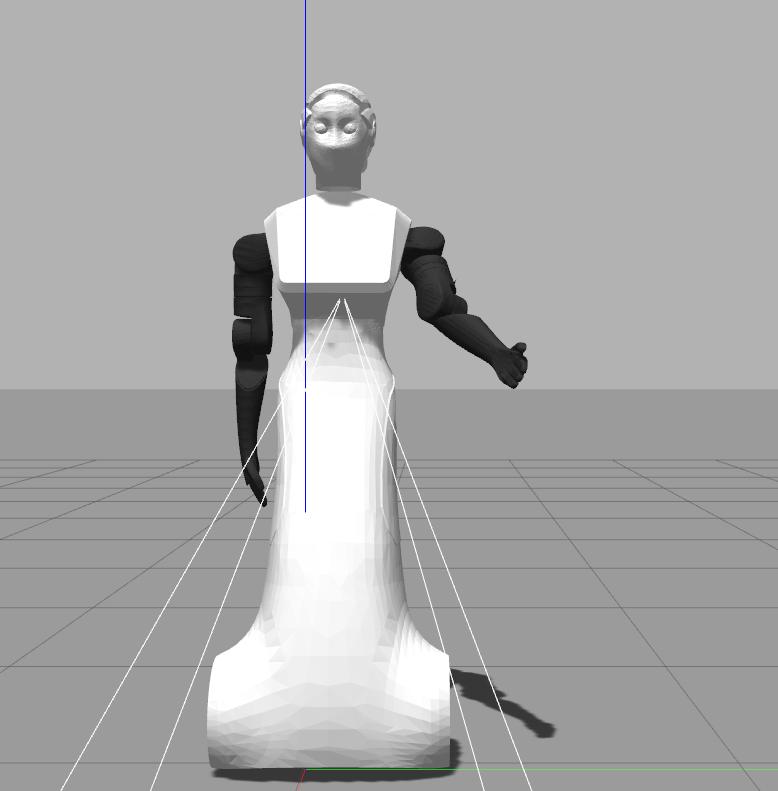
Now we are going to run an example that will bring ARI to the following joint space configuration of the left arm group:
arm_left_1_joint: 1.58 arm_left_2_joint: 0.33 arm_left_3_joint: -0.4 arm_left_4_joint: 0.77
Note that if we try to set the above kinematic configuration moving individual joints we will end up probably in a self-collision. The node that will take care to find a plan, i.e. a sequence of movements, to reach such a kinematic configuration is plan_left_arm_fk included in ari_moveit_tutorial package and has to be called as follows
rosrun ari_moveit_tutorial plan_left_arm_fk 1.58 0.33 -0.4 0.77
An example of plan executed by the node is depicted in the following sequence of images:
|
|
|
Inspecting the code
The code to implement such a node able to plan in joint space is shown below. Note that the key parts of the code are:
- Choose a group of joints
- Choose a planner
- Set initial and desired joint state
- Give time to find a plan
- Execute the plan if found
1 // ROS headers 2 #include <ros/ros.h> 3 4 // MoveIt! headers 5 #include <moveit/move_group_interface/move_group_interface.h> 6 7 // Std C++ headers 8 #include <string> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <map> 11 12 int main(int argc, char** argv) 13 { 14 ros::init(argc, argv, "plan_left_arm_fk"); 15 16 if ( argc < 5 ) 17 { 18 ROS_INFO(" "); 19 ROS_INFO("\tUsage:"); 20 ROS_INFO(" "); 21 ROS_INFO("\trosrun ari_moveit_tutorial plan_left_arm_fk arm_left_1_joint arm_left_2_joint arm_left_3_joint arm_left_4_joint"); 22 ROS_INFO(" "); 23 ROS_INFO("\twhere the list of arguments are the target values for the given joints"); 24 ROS_INFO(" "); 25 return EXIT_FAILURE; 26 } 27 28 std::map<std::string, double> target_position; 29 30 target_position["arm_left_1_joint"] = atof(argv[1]); 31 target_position["arm_left_2_joint"] = atof(argv[2]); 32 target_position["arm_left_3_joint"] = atof(argv[3]); 33 target_position["arm_left_4_joint"] = atof(argv[4]); 34 35 ros::NodeHandle nh; 36 ros::AsyncSpinner spinner(1); 37 spinner.start(); 38 39 std::vector<std::string> arm_left_joint_names; 40 //select group of joints 41 moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface group_arm_left("arm_left"); 42 //choose your preferred planner 43 group_arm_left.setPlannerId("SBLkConfigDefault"); 44 45 arm_left_joint_names = group_arm_left.getJoints(); 46 47 group_arm_left.setStartStateToCurrentState(); 48 group_arm_left.setMaxVelocityScalingFactor(1.0); 49 50 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < arm_left_joint_names.size(); ++i) 51 if ( target_position.count(arm_left_joint_names[i]) > 0 ) 52 { 53 ROS_INFO_STREAM("\t" << arm_left_joint_names[i] << " goal position: " << target_position[arm_left_joint_names[i]]); 54 group_arm_left.setJointValueTarget(arm_left_joint_names[i], target_position[arm_left_joint_names[i]]); 55 } 56 57 moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::Plan my_plan; 58 group_arm_left.setPlanningTime(5.0); 59 bool success = bool(group_arm_left.plan(my_plan)); 60 61 if ( !success ) 62 throw std::runtime_error("No plan found"); 63 64 ROS_INFO_STREAM("Plan found in " << my_plan.planning_time_ << " seconds"); 65 66 // Execute the plan 67 ros::Time start = ros::Time::now(); 68 69 moveit::planning_interface::MoveItErrorCode e = group_arm_left.move(); 70 if (!bool(e)) 71 throw std::runtime_error("Error executing plan"); 72 73 ROS_INFO_STREAM("Motion duration: " << (ros::Time::now() - start).toSec()); 74 75 spinner.stop(); 76 77 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 78 }
Note that when a plan is found and is executed with the following line of code
69 moveit::planning_interface::MoveItErrorCode e = group_arm_left.move();
The required control commands are sent to the left arm controller through its Action interface:
/arm_left_controller/follow_joint_trajectory/goal










